About 32,000 new cases of primary cancer of the pancreas were diagnosed in the U.S. in 2005, and as many people died from this disease. World incidence of pancreatic cancer was 232,306 in 2002. The vast majority of diagnosed cases are late stage and metastatic. Pancreatic cancer is almost uniformly deadly; five-year relative survival rates are approximately 4%, and, if left untreated, median survival is about 4 months. Although only 2% of cancers in the US are pancreatic, it is the 4th leading killer.
Surgery is the treatment of choice for early, resectable pancreatic cancer, but only 20% of tumors are resectable. External beam and intraoperative radiation therapy decrease local progression in patients with unresectable, locally advanced disease. Chemotherapy (typically with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or gemcitabine) has been used as an adjunct to radiation treatment.3
Using the CyberKnife® System to treat pancreatic cancer:
Two published studies by Koong et al.4,5 have shown that the CyberKnife® System, equipped with the Synchrony® Respiratory Tracking System, was capable of delivering therapeutic radiation with minimal toxicity to tumors in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Taken together, tumor progression was halted in 30 of 31 patients in these studies.
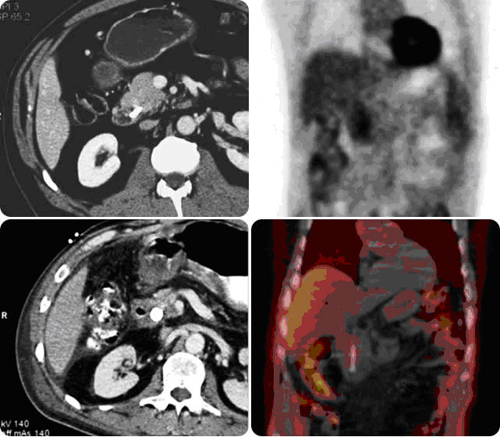
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
(Courtesy Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC)
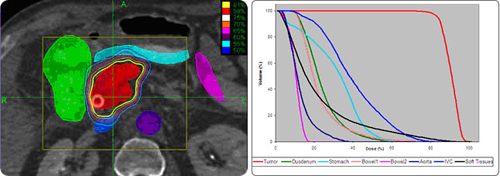
Axial CyberKnife® planning images and corresponding DVH with the tumor, isodose curves, and critical structures. The conformal dose distribution to the pancreas avoids the aorta (violet), vena cava (blue), duodenum (green), stomach (light blue) and bowel (pink and coral) as seen in these orthogonal views.
Axial CyberKnife® planning images and corresponding DVH with the tumor, isodose curves, and critical structures. The conformal dose distribution to the pancreas avoids the aorta (violet), vena cava (blue), duodenum (green), stomach (light blue) and bowel (pink and coral) as seen in these orthogonal views.
References
1.Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55(1):10-30. PubMed ABSTRACT
2.International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN 2002 Database Lyon, France, 2002. http://www-dep.iarc.fr/globocan/database.htm
3.Freelove R, Walling AD. Pancreatic cancer: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician 2006;73(3):485-92. PubMed ABSTRACT
4.Koong AC, Le QT, Ho A, Fong B, Fisher G, Cho C, et al. Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;58(4):1017-21.
5.Koong AC, Christofferson E, Le QT, Goodman KA, Ho A, Kuo T, et al. Phase II study to assess the efficacy of conventionally fractionated radiotherapy followed by a stereotactic radiosurgery boost in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;63(2):320-3. PubMed ABSTRACT